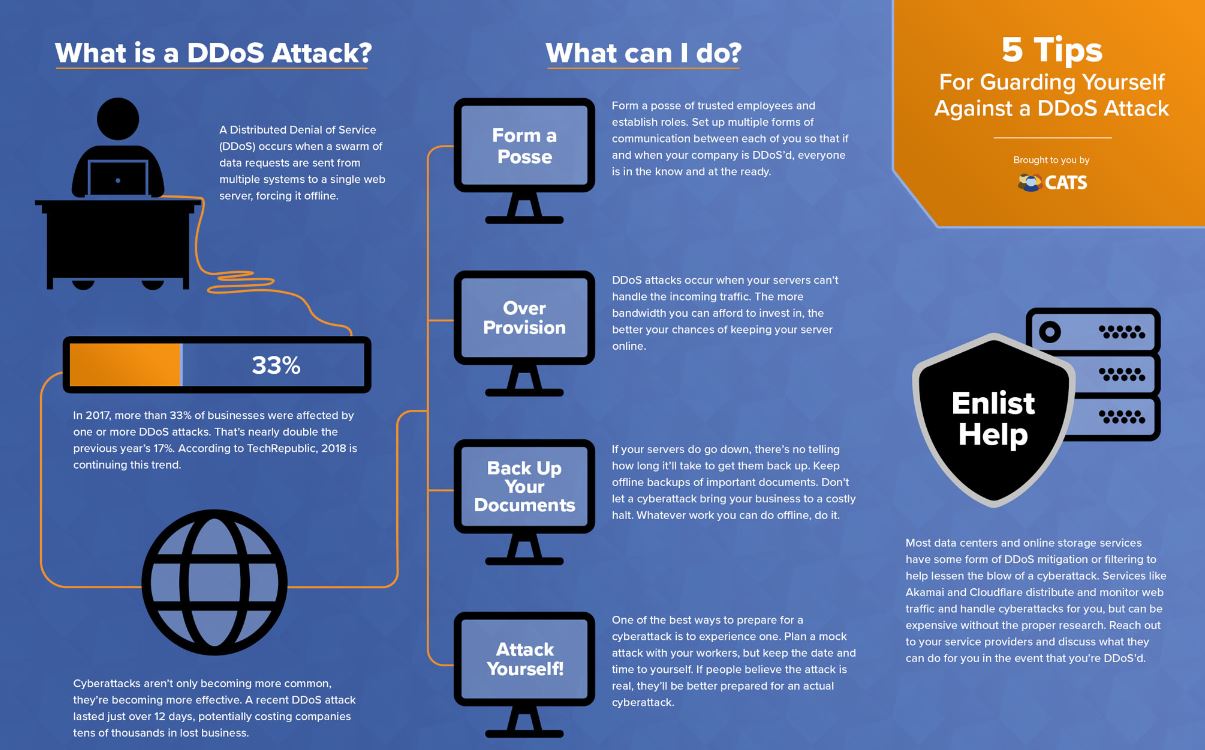
An IP stresser is a tool designed to test a network or server for robustness. The administrator may run a stress test in order to determine whether the existing resources (bandwidth, CPU, etc.) are sufficient to handle additional load.
Testing one’s own network or server is a legitimate use of an IP Stresser. Running it against someone else’s network or server, resulting in denial-of-service to their legitimate users, is illegal in most countries. So let’s dive into the roots of IP Stressers and DDos tools before we list the top 10 of 2020.
List of Contents
- What are booter services
- How are IP stresser’s different from Botnets
- Types of IP stresser and IP booter attacks
- What are common DOS/DDOS attacks
- Top 10 IP Stresser and IP Booters online (free only)
- Top 10 DDOS Tools
What are booter services?
Booters, also known as booter services, are on-demand DDoS (Distributed-Denial-of-Service) attack services offered by enterprising criminals in order to bring down websites and networks. In other words, booters are the illegitimate use of IP stressers.
Illegal IP Stresser’s often obscure the identity of the attacking server by use of proxy servers. The proxy reroutes the attacker’s connection while masking the IP address of the attacker.
Booters are slickly packaged as SaaS (Software-as-a-Service), often with email support and YouTube tutorials. Packages may offer a one-time service, multiple attacks within a defined period, or even “lifetime” access. A basic, one-month package can cost as little as $19.99. Payment options may include credit cards, Skrill, PayPal or Bitcoin (though PayPal will cancel accounts if malicious intent can be proved).
How are IP Stresser’s different from botnets?
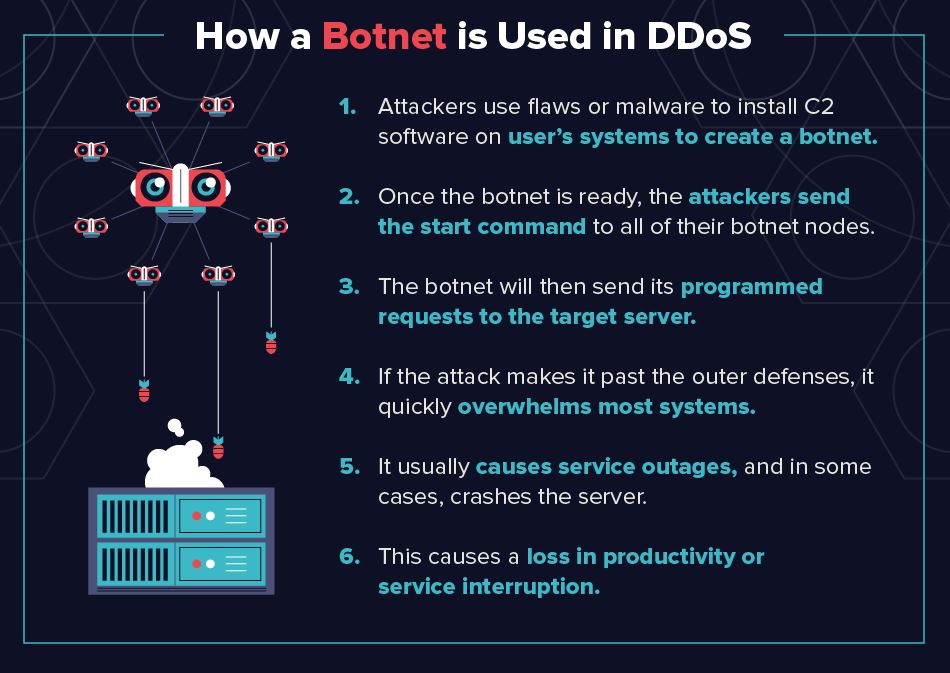
A botnet is a network of computers whose owners are unaware that their computers have been infected with malware and are being used in Internet attacks. Booters are DDoS-for-hire services.
Booters traditionally used botnets to launch attacks, but as they get more sophisticated, they are boasting of more powerful servers to, as some booter services put it, “help you launch your attack”.
Types of IP Stresser and IP Booter Attacks
Application Layer Attacks go after web applications, and often use the most sophistication. These attacks exploit a weakness in the Layer 7 protocol stack by first establishing a connection with the target, then exhausting server resources by monopolizing processes and transactions. These are hard to identify and mitigate. A common example is a HTTP Flood attack.
Protocol Based Attacks focus on exploiting a weakness in Layers 3 or 4 of the protocol stack. Such attacks consume all the processing capacity of the victim or other critical resources (a firewall, for example), resulting in service disruption. Syn Flood and Ping of Death are some examples.
Volumetric Attacks send high volumes of traffic in an effort to saturate a victim’s bandwidth. Volumetric attacks are easy to generate by employing simple amplification techniques, so these are the most common forms of attack. UDP Flood, TCP Flood, NTP Amplification and DNS Amplification are some examples.
What are common DOS/DDOS attacks?
The goal of DoS or DDoS attacks is to consume enough server or network resources so that the system becomes unresponsive to legitimate requests:
- SYN Flood: A succession of SYN requests is directed to the target’s system in an attempt to overwhelm it. This attack exploits weaknesses in the TCP connection sequence, known as a three-way handshake.
- HTTP Flood: A type of attack in which HTTP GET or POST requests are used to attack the web server.
- UDP Flood: A type of attack in which random ports on the target are overwhelmed by IP packets containing UDP datagrams.
- Ping of Death: Attacks involve the deliberate sending of IP packets larger than those allowed by the IP protocol. TCP/IP fragmentation deals with large packets by breaking them down into smaller IP packets. If the packets, when put together, are larger than the allowable 65,536 bytes, legacy servers often crash. This has largely been fixed in newer systems. Ping flood is the present-day incarnation of this attack.
- ICMP Protocol Attacks: Attacks on the ICMP protocol take advantage of the fact that each request requires processing by the server before a response is sent back. Smurf attack, ICMP flood, and ping flood take advantage of this by inundating the server with ICMP requests without waiting for the response.
- Slowloris: Invented by Robert ‘RSnake’ Hansen, this attack tries to keep multiple connections to the target web server open, and for as long as possible. Eventually, additional connection attempts from clients will be denied.
- DNS Flood: The attacker floods a particular domain’s DNS servers in an attempt to disrupt DNS resolution for that domain
- Teardrop Attack: The attack that involves sending fragmented packets to the targeted device. A bug in the TCP/IP protocol prevents the server from reassembling such packets, causing the packets to overlap. The targeted device crashes.
- DNS Amplification: This reflection-based attack turns legitimate requests to DNS (domain name system) servers into much larger ones, in the process consuming server resources.
- NTP Amplification: A reflection-based volumetric DDoS attack in which an attacker exploits a Network Time Protocol (NTP) server functionality in order to overwhelm a targeted network or server with an amplified amount of UDP traffic.
- SNMP Reflection: The attacker forges the victim’s IP address and blasts multiple Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) requests to devices. The volume of replies can overwhelm the victim.
- SSDP: An SSDP (Simple Service Discovery Protocol) attack is a reflection-based DDoS attack that exploits Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) networking protocols in order to send an amplified amount of traffic to a targeted victim.
- Smurf Attack: This attack uses a malware program called smurf. Large numbers of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) packets with the victim’s spoofed IP address are broadcast to a computer network using an IP broadcast address.
- Fraggle Attack: An attack similar to smurf, except it uses UDP rather than ICMP.
Also read: How to DDOS on PS4, Boot People Offline and Prevention
Top 10 IP Stresser and IP Booters Online (Free Only)
-
Synstresser
-
Stressthem
-
Fiberstresser
-
Stresser WTF
-
Free IP Stress
-
IP stresser
-
Muxbooter
-
DDOS Booter
-
PS4 Booter
-
Xbox Booter
Also read: How to DDOS on Xbox, Boot People Offline and Prevention
Top 10 DDOS Tools
1.LOIC
LOIC (Low Orbit ION cannon) is open-source software use for DDoS attack. This tool is written in C#. This tool sends HTTP, TCP, and UDP requests to the server.
Features:
- LOIC helps you to test the performance of the network.
- It enables you to create a DDoS attack against any site that they control.
- Loic does not hide an IP address even if the proxy server is not working.
- It helps you to perform stress testing to verify the stability of the system.
- This software can be used to identify programs that may be used by hackers to attack a computer network.
2.HOIC
High Orbit Ion Cannon is a free denial-of-service attack tool. It is designed to attack more than one URLs at the same time. This tool helps you to launch DDoS attacks using HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol).
Features:
- You can attack up to 256 websites at once.
- It has a counter that helps you to measure the output.
- It can be ported over to Linux or Mac OS.
- You can choose the number of threads in the current attack.
- HOIC enables you to control attacks with low, medium, and high settings.
3. HTTP Unbearable Load King (HULK)
HTTP Unbearable Load King (HULK) is a web server DDoS tool. It is specifically used to generate volumes of traffic at a webserver.
Features:
- It can bypass the cache server.
- This tool helps you to generate unique network traffic.
- HTTP Unbearable Load King (HULK) can be easily used for research purposes.
4. DDoSIM (DDoS Simulator)
DDoSIM (DDoS Simulator) is a tool that is used to create a distributed denial-of-service attack against a target server. It is written in C++ and can be used on the Linux operating system.
Features:
- This tool indicates the capacity of the server to handle application-specific DDOS attacks.
- It enables you to create full TCP connections to the target server.
- DDoSIM provides numerous options to perform a network attack.
- TCP connections can be flooded on a random network port.
5. RUDY (R U Dead Yet)
RUDY is a short form of R-U-Dead-Yet. It helps you to perform the DDoS attack with ease. It targets cloud applications by starvation of sessions available on the web server.
Features:
- This is a simple and easy tool.
- It automatically browses the target website and detects embedded web forms.
- R-U-Dead-Yet enables you to conduct HTTP DDoS attack using long-form field submission.
- This tool provides an interactive console menu.
- It automatically identifies form fields for data submission.
6. DAVOSET
DAVOSET is software for committing DDOS attacks via abuse of any website functionality. This command line tool helps you to commit distributed denial of service attacks without any hassle.
Features:
- It provides support for cookies.
- This tool provides a command-line interface to perform an attack.
- DAVOSET can also help you to hit attack using XML external entities (attack against an app that parses XML input).
7. GoldenEye
GoldenEye tool conducts a DDoS attack by sending an HTTP request to the server. It utilizes a KeepAlive message paired with cache-control options to persist socket connection busting.
Features:
- This tool consumes all the HTTP/S sockets on the application server for the DDoS attack.
- It is easy to use app written in Python.
- Arbitrary creation of user agents is possible.
- It randomizes GET, POST to get the mixed traffic.
8. PyLoris
PyLoris is a software product for testing network vulnerability by performing Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack online. It helps you to control poorly manage concurrent connections.
Features:
- It provides easy to use GUI (Graphic User Interface).
- This tool enables you to attack using HTTP request headers.
- It has the latest codebase (collection of source code used to build a particular software system).
- You can run PyLoris using Python script.
- This tool supports Windows, Mac OS, and Linux.
- It provides an advanced option having a limitation of 50 threads, each with a total of 10 connections.
9. OWASP HTTP Post
The OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project) HTTP Post software enables you to test your web applications for network performance. It helps you to conduct denial of service from a single machine.
Features:
- It allows you to distribute and transmit the tool with others.
- You can freely use this tool for commercial purposes.
- OWASP HTTP POST helps you to share the result under the license it provides.
- This tool enables you to test against the application layer attacks.
- It helps you to decide the server capacity.
10. Tor’s Hammer
Tor’s Hammer is an application-layer DDoS program. You can use this tool to target web applications and a web server. It performs browser-based internet request that is used to load web pages.
Features:
- It allows you to create rich text markup using Markdown (a plain text formatting syntax tool).
- Tor’s Hammer automatically converts the URL into links.
- This app uses web server resources by creating a vast number of network connections.
- You can quickly link other artifacts in your project.
- It holds HTTP POST requests and connections for 1000 to 30000 seconds.
Also read: Top 5 PS4 & XBOX IP Puller and IP Grabbers of 2020 (Free & Paid)